Portal:Mathematics
The Mathematics Portal
Mathematics is the study of representing and reasoning about abstract objects (such as numbers, points, spaces, sets, structures, and games). Mathematics is used throughout the world as an essential tool in many fields, including natural science, engineering, medicine, and the social sciences. Applied mathematics, the branch of mathematics concerned with application of mathematical knowledge to other fields, inspires and makes use of new mathematical discoveries and sometimes leads to the development of entirely new mathematical disciplines, such as statistics and game theory. Mathematicians also engage in pure mathematics, or mathematics for its own sake, without having any application in mind. There is no clear line separating pure and applied mathematics, and practical applications for what began as pure mathematics are often discovered. (Full article...)
Featured articles –
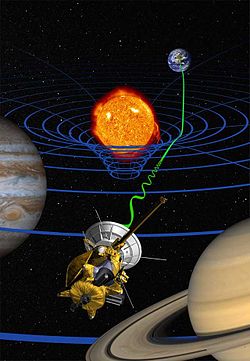
Selected image –

Good articles –
Did you know (auto-generated) –

- ... that Hong Wang's latest paper claims to have resolved the Kakeya conjecture, described as "one of the most sought-after open problems in geometric measure theory", in three dimensions?
- ... that multiple mathematics competitions have made use of Sophie Germain's identity?
- ... that the identity of Cleo, who provided online answers to complex mathematics problems without showing any work, was revealed over a decade later in 2025?
- ... that the discovery of Descartes' theorem in geometry came from a too-difficult mathematics problem posed to a princess?
- ... that Fathimath Dheema Ali is the first Olympic qualifier from the Maldives?
- ... that the word algebra is derived from an Arabic term for the surgical treatment of bonesetting?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
More did you know –

- ...the Piphilology record (memorizing digits of Pi) is 70000 as of Mar 2015?
- ...that people are significantly slower to identify the parity of zero than other whole numbers, regardless of age, language spoken, or whether the symbol or word for zero is used?
- ...that Auction theory was successfully used in 1994 to sell FCC airwave spectrum, in a financial application of game theory?
- ...properties of Pascal's triangle have application in many fields of mathematics including combinatorics, algebra, calculus and geometry?
- ...work in artificial intelligence makes use of swarm intelligence, which has foundations in the behavioral examples found in nature of ants, birds, bees, and fish among others?
- ...that statistical properties dictated by Benford's Law are used in auditing of financial accounts as one means of detecting fraud?
- ...that modular arithmetic has application in at least ten different fields of study, including the arts, computer science, and chemistry in addition to mathematics?
Selected article –
 |
| Johannes Kepler Image credit: User:ArtMechanic |
Johannes Kepler (1571 – 1630) was an Austrian Lutheran mathematician, astronomer and a key figure in the 17th century astronomical revolution. He is best known for his laws of planetary motion, based on his works Astronomia nova and Harmonice Mundi; Kepler's laws provided one of the foundations of Isaac Newton's theory of universal gravitation. Before Kepler, planets' paths were computed by combinations of the circular motions of the celestial orbs; after Kepler astronomers shifted their attention from orbs to orbits—paths that could be represented mathematically as an ellipse.
During his career Kepler was a mathematics teacher at a Graz seminary school (later the University of Graz, Austria), an assistant to Tycho Brahe, court mathematician to Emperor Rudolf II, mathematics teacher in Linz, Austria, and adviser to General Wallenstein. He also did fundamental work in the field of optics and helped to legitimize the telescopic discoveries of his contemporary Galileo Galilei.
Kepler lived in an era when there was no clear distinction between astronomy and astrology, while there was a strong division between astronomy (a branch of mathematics within the liberal arts) and physics (a branch of the more prestigious discipline of philosophy). (Full article...)
| View all selected articles |
Subcategories

Algebra | Arithmetic | Analysis | Complex analysis | Applied mathematics | Calculus | Category theory | Chaos theory | Combinatorics | Dynamical systems | Fractals | Game theory | Geometry | Algebraic geometry | Graph theory | Group theory | Linear algebra | Mathematical logic | Model theory | Multi-dimensional geometry | Number theory | Numerical analysis | Optimization | Order theory | Probability and statistics | Set theory | Statistics | Topology | Algebraic topology | Trigonometry | Linear programming
Mathematics | History of mathematics | Mathematicians | Awards | Education | Literature | Notation | Organizations | Theorems | Proofs | Unsolved problems
Topics in mathematics
| General | Foundations | Number theory | Discrete mathematics |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
| Algebra | Analysis | Geometry and topology | Applied mathematics |
Index of mathematics articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Related portals
WikiProjects
![]() The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
The Mathematics WikiProject is the center for mathematics-related editing on Wikipedia. Join the discussion on the project's talk page.
In other Wikimedia projects
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus